In industrial settings, choosing the right perforated metal sheet is a decision driven by function — strength, airflow, filtration, weight and manufacturability. This article compares square-hole and round-hole perforated metal sheets from a structural and practical point of view, focusing on industrial use cases such as machine guards, ventilation panels, filtration supports and load-bearing safety grating.
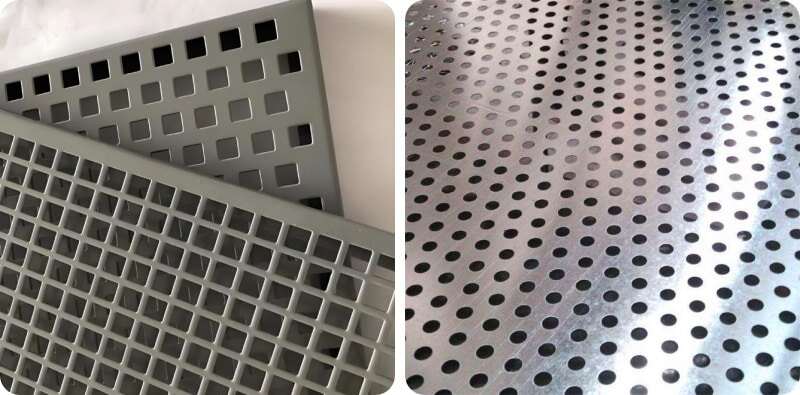
1. Basic geometry and why it matters
Hole geometry defines more than appearance. The shape and edge orientation of each hole affect local stress concentration, stiffness, and the net cross-section left in the parent plate.
- Round holes have smooth edges and lower stress-concentration factors. They are easier to punch with minimal burrs and tend to perform better under cyclic loading where fatigue is a concern. For many ventilation and acoustic panels, round perforations offer excellent airflow with predictable structural behavior. See our round hole perforated metal sheet product page for common patterns and sizes.
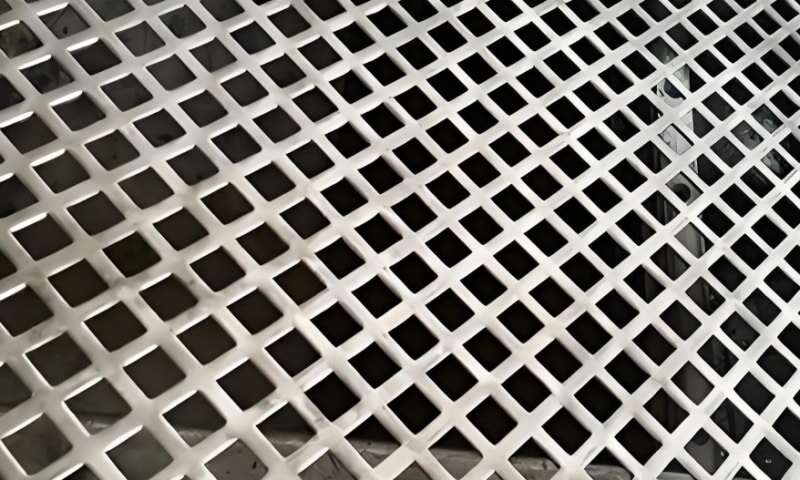
- Square holes provide straighter edges and a different load path across the sheet. Because square holes remove material in a more angular pattern, the remaining ribs between holes can create a stiffer local lattice in one direction — an advantage for applications requiring directional stiffness or a flat load-bearing surface.
2. Stiffness and load capacity
When an industrial floor panel, machine guard, or platform carries a load, the effective stiffness of the perforated panel is critical.
- At equivalent open area, square-hole arrays often yield greater in-plane stiffness in the axis aligned with the hole edges, because the remaining metal ribs are broader in those directions. This can mean less deflection under uniform load.
- Round holes typically allow slightly higher tensile strength per ligament area due to smoother ligament transitions, and they distribute local stress more evenly — beneficial for repeated impact or vibration.
Practical tip: For heavy, distributed loads where deflection must be minimized (e.g., platform panels and certain safety grating), consider square-hole patterns in thicker carbon steel sheets. For dynamic or fatigue-sensitive environments, round holes in well-finished stainless or carbon steel can outlast angular designs.
3. Open area, airflow and filtration performance
Open area (percentage of hole area vs total panel area) directly affects airflow, filtration performance and acoustic properties.
- For the same nominal diameter/side and pitch, round holes usually offer smoother flow paths and slightly higher permeability per unit open area.
- Square holes can achieve high open area too, and their straight edges may help in coarse filtration or sieving roles where particle capture geometry matters.

Application example: In an industrial ventilation hood, a round-hole perforated panel in galvanized steel provides balanced airflow and corrosion resistance. If the design needs a flat surface for mounting equipment, a square-hole pattern in carbon steel may be preferred. Check our carbon steel perforated metal sheet options for thicknesses and pitches used in heavy industry.
4. Manufacturing and finishing considerations
Manufacturing cost and achievable tolerances influence the final choice.
- Punching round holes is generally faster and produces less tool wear. Edge burrs are easier to control.
- Square holes require tighter tool alignment and sometimes secondary trimming to ensure clean corners, slightly increasing cost for very fine patterns.
Materials like galvanized steel, stainless steel, aluminum or high-manganese steel each interact differently with hole geometry. For example, galvanized round-hole panels are common where corrosion resistance and ventilation matter, while high-manganese perforated sheets might be selected for heavy-impact environments (conveyors, crushers).
5. Safety grating and load-bearing panels
When safety and slip resistance matter — for walkways and platforms — the pattern and remaining Rib geometry determine both strength and traction.
- Perforated panels used as safety grating often combine hole geometry with serrated edges or raised patterns. Our perforated safety grating ranges show typical solutions where load rating and slip resistance are engineered together.
6. Choosing the right option — summary checklist
Use this quick checklist when selecting between square and round perforated sheets:
- Need directional stiffness / minimal deflection → Square holes, thicker gauge.
- Need even stress distribution, fatigue resistance → Round holes, smooth ligaments.
- Primary goal is airflow/filtration with simple manufacture → Round holes.
- Want a flatter bearing surface or engineered aesthetic for mounting → Square holes.
- Corrosion or chemical exposure → choose material first (galvanized/stainless/aluminum), then hole type.
7. Final recommendation for industrial buyers
For industrial procurement, define the functional priorities (load, fatigue life, airflow, corrosion) and then select hole geometry and material to match. If you need custom pitches, hole diameters, thickness or batch sizes, our factory can produce one-piece prototypes or large runs and tailor each variable to your spec. Learn more about our manufacturing capabilities and custom options on the homepage for Chinese-factory customized Perforated Metal Sheets – Customized by Chinese Factories: https://perfsheet.com.












