Machine guards do more than keep hands and tools out of danger — when designed well they protect equipment, manage heat, and help maintain reliable airflow. Among perforation patterns, the hexagonal (honeycomb) layout strikes a rare balance of open area, structural strength, and predictable flow behavior. This article explains why hexagonal perforated metal sheets work so well in mechanical guards, how to choose hole size, thickness and material, and practical tips for turning an idea into a production-ready guard.
Why the hexagonal pattern improves airflow
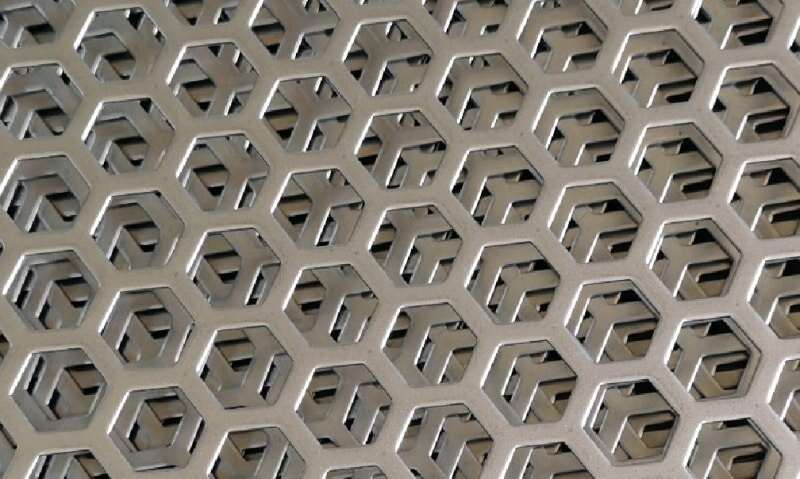
Hexagonal (honeycomb) perforations are closer to the ideal of packing identical circular openings with minimal wasted space. Compared to single-row square or staggered round patterns, hex layouts can:
- Achieve a higher open area for the same hole diameter and pitch, which directly lowers pressure drop across the guard.
- Maintain better structural rigidity, letting you use thinner gauges while keeping the sheet stiff — useful for lightweight fan guards.
- Produce a more uniform flow profile across the guarded opening because the holes are arrayed in a densely packed, consistent geometry.
- Reduce small-scale turbulence and vortex shedding that can generate noise when air passes rapidly through irregular openings.
All those advantages combine into improved cooling efficiency for enclosures and motors, quieter operation near fans, and lower energy loss from restricted flow.
Practical benefits for mechanical guards
When a guard’s job is to protect personnel while minimizing impact on the machine’s cooling or ventilation, hexagonal perforated sheets deliver:
- Lower pressure drop — better cooling and reduced fan load.
- Noise reduction — smoother flow through multiple small, evenly spaced holes often reduces whistling and tonal noise.
- Consistent filtration/straining — captures large debris while allowing air to pass uniformly.
- Aesthetic and durable finish — available in stainless steel, aluminum, galvanized and coated finishes for long life in industrial settings.
You can see real product examples like a hexagonal perforated metal sheet installed as a fan guard, or choose Perforated Safety Grating for heavy-duty walkway protection where air exchange matters.
How to choose hole diameter, open area and thickness
Selecting the right geometry starts from the application — fan cooling, dust exclusion, acoustic shielding, or purely mechanical protection. Use these design rules of thumb:
- Hole diameter vs. particulate size: If you need to block debris, pick a hole size smaller than the largest expected debris. For cooling-only guards, larger holes (with higher open area) are better.
- Open area target: For forced-air fan guards, aim for as large an open area as practical — many applications benefit from 30–60% open area. Hex patterns often reach higher open area at equal hole size than square patterns.
- Thickness and span: Thinner sheets reduce weight but may deflect under impact. Use thicker gauges or add framing for spans over a few inches. Materials like <a href=”/products/stainless-steel-perforated-sheet”>stainless steel perforated sheets</a> give strength plus corrosion resistance.
- Edge and mounting details: Leave enough material for secure mounting; countersunk screws or captive clips work well. Consider folded edges to increase stiffness without extra gauge.
When you need very fine control — for example low-noise enclosures or lab equipment — micro-hole hex patterns or a combination of micro-perforated layers can be used to tune flow resistance and acoustic attenuation. See product options like micro-perforated metal sheets.
Materials and finish choices
Material affects manufacturability, corrosion resistance, and cost:
- Stainless steel — best for corrosive or food-industry settings. Durable and easy to clean.
- Aluminum — lightweight, excellent for mobile equipment, and non-magnetic.
- Galvanized steel — cost-effective for outdoor or industrial environments where some corrosion resistance is needed.
- Carbon or high-manganese steel — for heavy-duty guards and impact resistance.
Choose powder coating or specialty finishes if aesthetics or additional corrosion protection are priorities.
Fabrication and production considerations
Because hexagonal patterns pack efficiently, they are well-suited to high-volume punch-production. But other fabrication notes matter:
- Punching vs. laser: Punching is fast and economical for high-volume standard patterns; laser cutting gives flexibility for custom hole shapes or small batches.
- One-piece minimums: If you need single-piece prototyping or small runs, make use of suppliers who support one-piece minimum orders and custom dimensions.
- Edge treatment: Deburring and edge folding improve safety and fit. For machine guards, folded edges are common to reduce sharpness and add stiffness.
If you want to compare pattern options, look at variations such as round hole, square hole, or slotted perforated patterns and evaluate them against the hexagonal option for your target open area and strength.
Typical specifications and examples
Here are starting points often used when engineering a hex perforated guard:
- Fan guard for 120 mm fan: hole diameter 4–6 mm, open area ~40–50%, sheet thickness 0.8–1.2 mm.
- Motor vent panel: hole diameter 6–10 mm, open area 45–60%, stainless or galvanized finish, thickness 1.0–2.0 mm plus frame.
- Heavy-duty protective screen: hex holes 10–20 mm, thicker gauges (2–4 mm) or safety grating hybrid for impact resistance.
Work with your fabricator to test a prototype: even small changes in pitch or hole size can affect cooling and noise.
Conclusion — design for flow, protect for life
Hexagonal perforated sheets are an excellent choice for mechanical guards when you need a balance of airflow, strength, and clean aesthetics. They let you preserve cooling performance and reduce noise while meeting safety and durability requirements. By picking the right hole size, open area and material, you can optimize fan performance, extend motor life, and keep operators safe.
If you’d like help sizing a hexagonal perforated guard, comparing materials, or getting a custom sample, contact us at info@perfsheet.com — one-piece prototypes and high-volume production both supported.












