When selecting a 304 perforated metal sheet for a ventilation or airflow project, buyers often focus on thickness, hole diameter, and material. What many overlook is the open area ratio—the percentage of open space created by perforated holes across the metal surface. This ratio can significantly influence wind resistance, airflow, pressure drop, durability, and acoustic performance.
In procurement discussions, engineers and buyers frequently ask how open area affects ventilation results. Understanding this relationship can help avoid oversizing fans, reduce operational costs, and improve long-term performance.
Stainless Steel Perforated Metal Sheets
Stainless steel perforated metal sheets offer exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for both aesthetic and functional uses in various industries.
What Is Open Area Ratio?
The open area ratio refers to the percentage of perforated opening area relative to the total sheet area.
The higher the open area ratio, the more air can flow through the sheet. For example, a sheet with a 10% open area blocks far more air than one with a 40% open area.
This ratio depends on:
- hole diameter
- center-to-center spacing
- perforation pattern
- sheet thickness
A small change in hole size or spacing can produce a major change in airflow performance.
Why 304 Stainless Steel Performs Well in Ventilation Systems
304 stainless steel perforated sheets are selected for industrial ventilation because of:
- corrosion resistance
- strength under pressure
- clean, aesthetic appearance
- structural stability
They are widely used in HVAC equipment, machinery guards, building ventilation louvers, and architectural facades.
Open Area Ratio and Its Impact on Wind Resistance
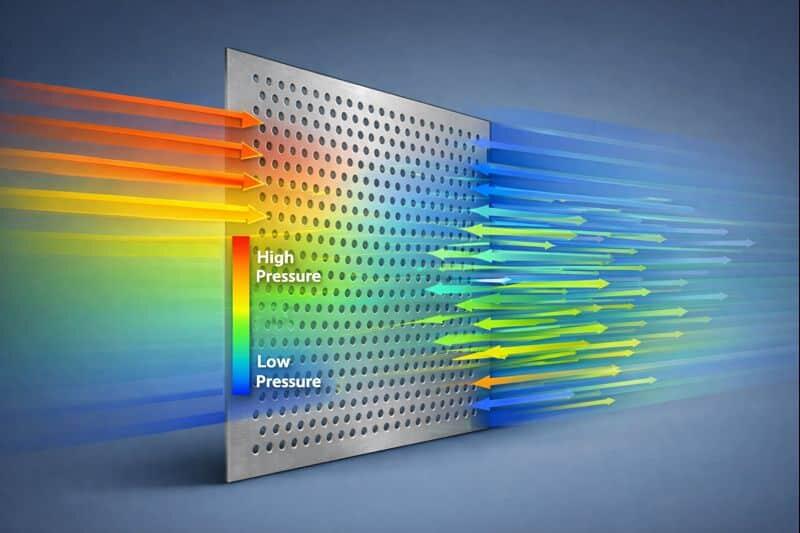
When air hits a perforated sheet, each hole becomes a “micro channel.” The sheet acts as a partial barrier. As the open area increases, resistance drops because more air can pass through freely.
Typical airflow observations with standard hole patterns:
| Open Area Ratio | Wind Resistance |
|---|---|
| 10–20% | Very high resistance |
| 20–35% | Moderate resistance |
| 35–60% | Improved airflow |
| 60%+ | Very low resistance |
Higher open area improves ventilation, but decreases mechanical strength and may require stronger support structures depending on application.
How Open Area Affects Ventilation Performance
Engineers frequently evaluate airflow pressure loss through perforated sheet barriers. A higher open area ratio typically results in:
- lower air pressure drop
- reduced ventilation energy costs
- increased equipment efficiency
- better thermal dissipation
For industrial ventilation, open areas between 30–55% often provide a balance of structural integrity and strong airflow performance.
Real-world examples shared by ventilation equipment manufacturers show that airflow resistance may decrease by over 40% when increasing open area from 15% to 40%, depending on flow velocity and sheet thickness.
Balancing Open Area and Strength Requirements
Although high open area ratios support ventilation, they also reduce sheet strength and load capacity.
Buyers should consider:
- sheet thickness
- hole diameter
- hole spacing
- material grade
- expected wind load or fan pressure
Using thicker sheet material allows higher open area without excessive deformation under air pressure or vibration.
Hole Shape and Pattern Influence Airflow Behavior
Open area ratios are directly influenced by hole shape and layout. Common choices include round, square, slotted, and decorative patterns.
Customer decisions typically balance:
- airflow efficiency
- visual effects
- drainage capability
- directional airflow needs
Round holes generally provide the most uniform flow and predictable resistance, making them favorable for ventilation systems.
Guidelines for Choosing the Right Open Area for Ventilation Projects
When selecting a 304 perforated metal sheet, consider:
- internal vs. external airflow exposure
- expected wind load or fan pressure
- required ventilation rate
- safety requirements
- corrosion concerns
- noise attenuation needs
General purchasing recommendations:
- Low ventilation needs → 10–25% open area
- Moderate ventilation → 25–40% open area
- Maximum ventilation efficiency → 40–60%+ open area
For large areas or high-pressure airflow, reinforcement or thicker material should be considered to maintain structural integrity.
FAQs About Open Area Ratio and Ventilation Performance
Does a higher open area always mean better ventilation?
In many cases yes, but not always. Structural strength and noise control must also be considered.
How do I calculate appropriate open area for my system?
Buyers should evaluate airflow volume, fan power, expected wind pressure, and structural requirements.
Can perforation patterns affect airflow direction and pressure?
Yes. Certain slotted patterns can redirect flow, while staggered holes improve uniform airflow.

Ready to Source Custom 304 Perforated Metal Sheets?
When selecting materials for ventilation systems, the open area ratio plays a critical role in balancing airflow and structural performance. Properly chosen perforation patterns help reduce energy consumption, lower noise, and improve temperature regulation.
If you require guidance selecting hole size, spacing, sheet thickness, or open area ratio for your application, you can request technical support or a quotation.
Contact Us for Custom Orders
Whether you are seeking a prototype order or bulk production, support is available for multiple hole sizes, thicknesses, materials, and custom tooling.
To request a quote or consultation, contact:
info@perfsheet.com
We will respond within 24 hours.













