Choosing Round Hole Punched Panels for Machine Guarding and Industrial Equipment
Selecting the right perforated metal for a machine guard is rarely about one parameter. Industrial equipment builders must balance safety regulations, airflow performance, acoustic behavior, visibility, structural rigidity, and procurement requirements. As a result, many OEM buyers rely on Custom Round Hole Punched Panels because round-hole geometry provides predictable safety performance, consistent fabrication tolerances, and broad application flexibility across both structural and ventilation panels.
Hole Diameter and Protective Distance Requirements
In machine guarding, safety reach is governed by hole diameter, not open area. Larger openings in Round Hole Punched Panels allow deeper finger insertion, which increases the protective distance required between the guard and the moving hazard. Standards such as ISO 13857 and OSHA machineguarding guidelines define these distances, and compliance depends on selecting a hole diameter that limits the maximum insertion depth.
For this reason, OEMs often specify small-to-medium hole diameters in Round Hole Machine Guard Panels while maintaining a pattern that still supports cooling and visibility.
Open Area and Airflow Performance
Open area plays a central role in airflow, thermal dissipation, and internal equipment cooling. Higher open area improves ventilation, reduces pressure drop, and supports the performance of forced-air cooling systems. For electronic enclosures, HVAC components, or motor housings, Perforated Round Hole Panels with optimized open area can significantly enhance thermal stability without compromising serviceability.
This is why many buyers choose Custom Round Hole Punched Panels that target a specific open-area range rather than adjusting hole diameter alone.
Acoustic Behavior and Visibility
Round hole perforations remain the most consistent and predictable shape for achieving acoustic transparency. Higher open area allows sound energy to pass through the guard, which is useful when equipment relies on audible alarms or requires operator communication. When noise reduction is needed, the perforated panel is often paired with an acoustic liner rather than changing the perforation geometry.
Visibility also improves with open area, allowing operators to inspect belts, couplings, and mechanical components without removing the guard.
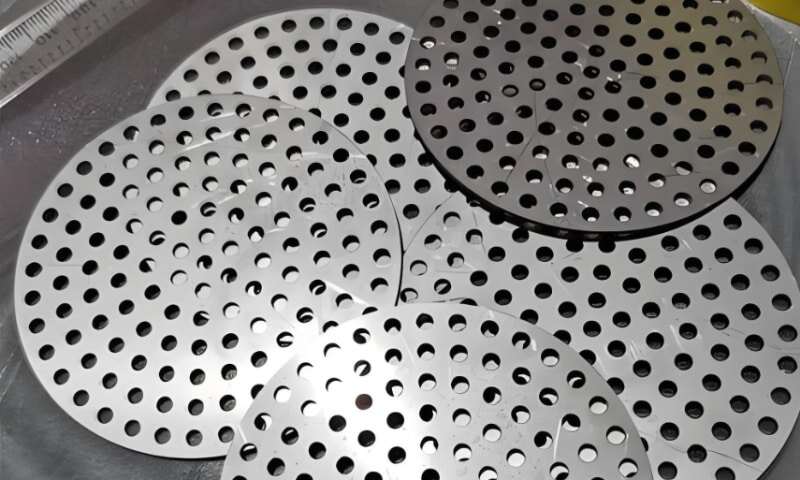
Filtration and Particulate Control
Controlling dust, debris, or process particulate requires balancing both hole diameter and open area. Smaller holes provide better particulate control, but airflow depends on the total aperture ratio. For sanitation-critical or dust-sensitive environments, Round Hole Punched Panels are often combined with wire mesh, a fine perforated liner, or filter media to meet hygiene or filtration requirements without compromising cooling.
Material Selection for Structural and Ventilation Panels
For structural machine guards, carbon steel is widely used for its rigidity, impact resistance, and cost efficiency. Where corrosion resistance, weight reduction, or easier forming is required, 5052 aluminum is a strong choice. It is also common for OEMs to standardize Custom Round Hole Punched Panels across both materials to maintain visual consistency on multi-panel assemblies.
For thinner ventilation or acoustic panels, aluminum and stainless steel provide excellent stability, clean surface finishes, and efficient fabrication.
Matching Panel Thickness to the Application
Industrial buyers typically separate their perforated panel requirements into two application categories:
- Structural Guarding Panels: medium-to-thick gauges designed for impact resistance
- Ventilation or Acoustic Panels: lighter gauges optimized for airflow or sound transparency
Mixed applications—common in automated machinery, conveyors, packaging equipment, and electronics housings—often require both types on the same machine platform. This makes consistency of pattern, tolerances, and finishing across all Round Hole Punched Panels especially important.
Procurement Considerations for OEM and Industrial Buyers
When preparing an RFQ for Custom Round Hole Punched Panels, procurement teams typically evaluate:
- hole diameter, pitch, and open area
- material grade and thickness
- fabrication tolerances
- expected load and stiffness
- bending or forming requirements
- coating or finishing
- compliance with ISO/OSHA guarding standards
Prototyping remains a best practice, helping validate airflow, stiffness, and usability before finalizing production.
Round Hole Perforated Metal Sheets
Custom perforated metal sheets with precise hole patterns in various materials: stainless steel, aluminum, galvanized steel, carbon steel, copper, brass, and plastic. Durable and corrosion-resistant.
Perfect for architectural screens, machinery guards, acoustic panels, and decorative elements. Factory-direct pricing with cutting/bending services. Request quote or sample today.
Summary: How to Select the Right Round Hole Punched Panels
For industrial machine guarding:
- Hole diameter determines safety reach
- Open area determines airflow and visibility
- Material and thickness determine stiffness and durability
- Secondary liners support filtration and hygiene
- Consistent tolerances support modular OEM assembly
By balancing these factors, OEMs and equipment builders can specify Custom Round Hole Punched Panels that deliver the right combination of safety, cooling, acoustics, strength, and cost efficiency.













